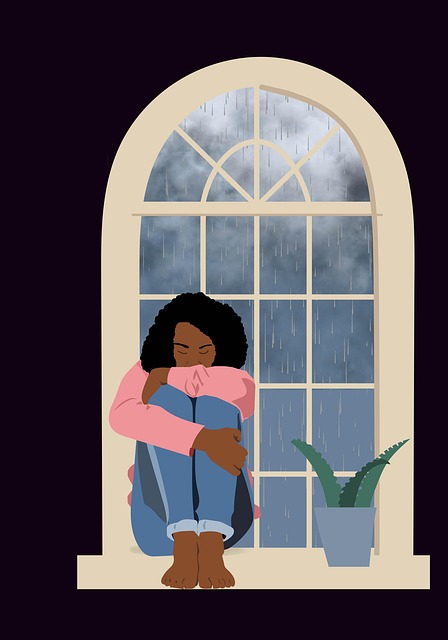
Stress can significantly impact young minds, leading to various issues like learning difficulties, behavior problems, and mental health concerns. Early intervention through therapy, such as play therapy and cognitive-behavioral techniques (CBT), is vital to prevent chronic stress from escalating into severe problems like substance abuse or drug dependence. CBT and play therapy, combined with self-care practices like mindfulness and relaxation techniques, equip young individuals with coping mechanisms for stress management. Recognizing behavioral changes in children can indicate drug-related stress, prompting early intervention and targeted therapy to enhance emotional intelligence and reduce future substance misuse risks. Comprehensive education and screening programs address rising youth substance abuse trends, fostering healthy development through safe environments and evidence-based practices.
Stress management techniques teaching play a pivotal role in fostering healthy development among young minds. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted aspects of understanding and addressing stress, especially as it pertains to children. We explore the impact of stress on young lives and its potential links to drug-related issues. Through identifying signs of substance abuse-related stress, we empower parents and caregivers with effective therapy approaches and preventive measures to support at-risk children.
- Understanding Stress and Its Impact on Young Minds
- Identifying Signs of Drug-Related Stress in Children
- Effective Therapy Approaches for Stress Management
- Preventive Measures and Support Systems for At-Risk Children
Understanding Stress and Its Impact on Young Minds

Stress is an inevitable part of life, but its impact on young minds can be profound. Young children are still developing their emotional and cognitive abilities, making them more susceptible to the adverse effects of stress. Prolonged or chronic stress can lead to difficulties in learning, behavior problems, and even mental health issues like anxiety and depression. It’s crucial to recognize that stress management isn’t just about teaching kids to cope; it’s also about fostering their inner strength and resilience.
Early intervention is key to preventing the escalation of stress into more severe issues such as substance abuse or drug dependence. Therapy for young children, including play therapy and cognitive-behavioral techniques, can be highly effective in helping them understand and manage their emotions. Mental wellness podcast series production often includes empathy building strategies that encourage open communication and emotional intelligence—essential tools for navigating life’s challenges. By equipping young individuals with these skills, we empower them to develop a healthy mindset and build lasting inner strength.
Identifying Signs of Drug-Related Stress in Children

Recognizing signs of drug-related stress in children is an essential aspect of early intervention and prevention. Youngsters exposed to substance abuse may exhibit a range of behavioral and emotional changes indicative of underlying issues. Mental health professionals play a crucial role in identifying these subtle cues, which can be as diverse as heightened anxiety, sudden changes in mood, or withdrawal from social activities.
Through therapy for young children struggling with drug abuse, mental health awareness is fostered, and risk management planning becomes more effective. By promoting emotional intelligence, professionals can equip children with coping mechanisms to navigate stress, thereby reducing the chances of substance misuse. Early detection and appropriate support can significantly impact a child’s overall well-being and future mental health resilience.
Effective Therapy Approaches for Stress Management

In teaching stress management techniques, particularly to young children, certain therapeutic approaches have proven highly effective. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a popular method that helps kids identify and change negative thought patterns contributing to stress. By understanding how their thoughts influence emotions and behaviors, children can develop coping strategies tailored to their unique needs. Play therapy, another powerful tool, offers a non-verbal approach for younger kids who may struggle with expressing their feelings verbally.
In addition to CBT and play therapy, integrating self-care practices into the curriculum is essential for risk management planning among mental health professionals. Teaching mindfulness exercises, deep breathing techniques, and progressive muscle relaxation can empower young individuals to manage stress independently. Moreover, addressing substance abuse issues early through comprehensive education and screening programs can prevent the escalation of problems, especially in light of drug abuse and substance abuse trends among youth.
Preventive Measures and Support Systems for At-Risk Children

At-risk children often require early intervention to mitigate stress and prevent long-term mental health issues. Preventive measures in early childhood focus on fostering a safe, nurturing environment that promotes healthy development. This includes implementing Mind Over Matter principles, teaching coping skills development, and encouraging empathy building strategies within the family unit and at school. Early therapy for young children struggling with drug abuse or substance abuse can play a pivotal role in breaking negative cycles and providing essential support systems.
By integrating evidence-based practices, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, educators and caregivers can help children develop effective stress management techniques tailored to their unique needs. These interventions not only address immediate concerns but also equip young individuals with lifelong tools to navigate challenging situations, thereby enhancing their resilience and overall well-being.
Stress management techniques are invaluable tools for young minds, especially in navigating the challenges of drug abuse and substance addiction. By understanding stress impacts on children, identifying warning signs early, adopting effective therapy approaches, and fostering robust support systems, we can empower them to lead healthier, happier lives. These strategies not only mitigate risks but also promote resilience, ensuring a brighter future for our young individuals.